The Vital Importance of Creating Native Habitats for Diverse Wildlife and Pollinators.
Our planet has witnessed a rapid decline in biodiversity, threatening the delicate balance of ecosystems worldwide. As we continue to urbanize and modify natural landscapes, creating native habitats for a diverse range of wildlife and pollinators becomes increasingly crucial.
Emphasizing the importance of preserving and restoring these habitats is essential to safeguarding the future of our planet’s ecosystems and the countless species that depend on them.
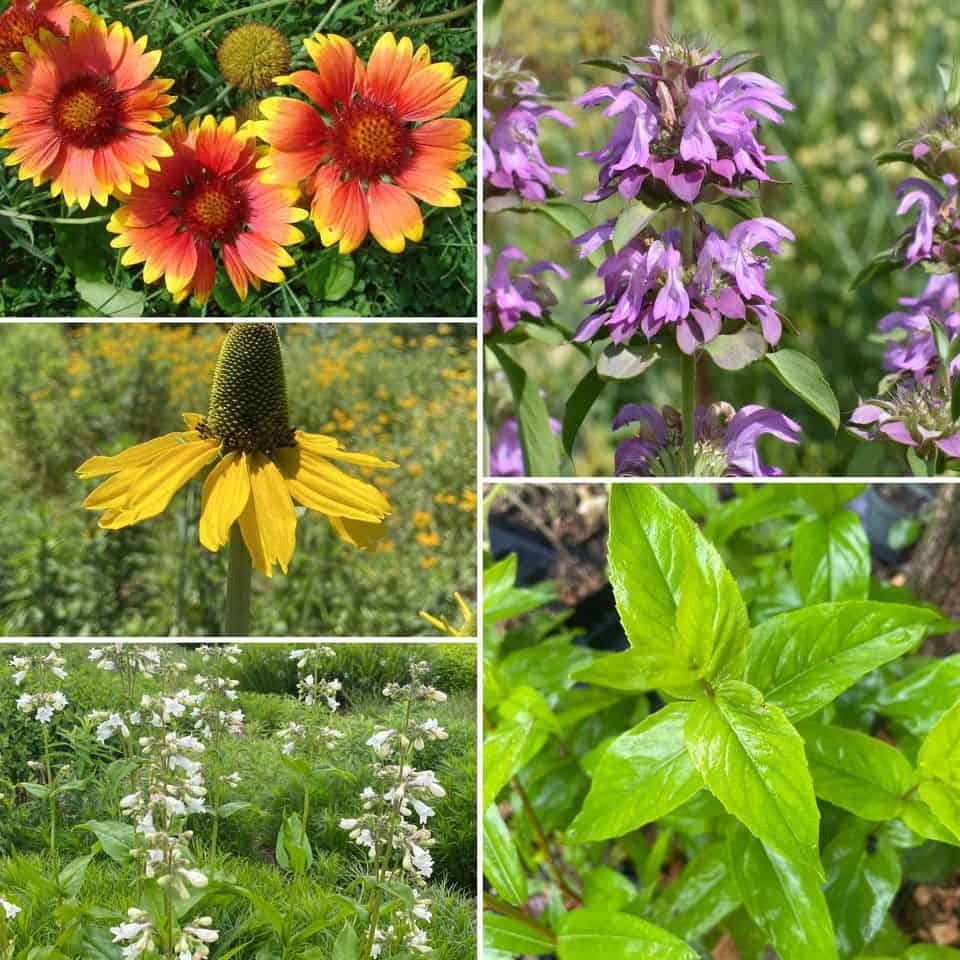


Preserving Biodiversity through Native Habitats
Preserving biodiversity is crucial for the health of our planet and the survival of countless plant and animal species. One effective way to achieve this is by creating and maintaining native habitats that cater to the unique needs of different species. By doing so, we offer a lifeline to these organisms, enabling them to thrive and flourish.
When we promote diverse landscapes that mirror the natural homes of various species, we effectively support local wildlife populations. By ensuring that these habitats have the necessary resources, such as food, water, and shelter, we encourage the survival and growth of these populations.
Native habitats play a pivotal role in safeguarding endangered species. By providing them with sanctuaries to recuperate and reproduce, we increase their chances of survival and contribute to their recovery. This, in turn, has a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem, leading to increased stability and a healthier balance of species interactions.
Moreover, these habitats benefit the flora, fauna, and human communities. Native habitats can enhance the overall health of our ecosystems, ensuring cleaner air, water, and soil, and even providing opportunities for ecotourism and educational programs that foster environmental awareness.
By actively preserving and expanding native habitats, we take a significant step toward supporting overall biodiversity and combating the threats of habitat loss and species extinction. It is a collective responsibility that requires the efforts of governments, organizations, and individuals alike, working together to create a sustainable and thriving future for our planet and all its inhabitants
Ecological balance and resilience
Ecological balance and resilience are fundamental aspects of native habitats, offering a level of interconnectedness that is challenging to replicate in artificially constructed environments. These natural ecosystems embody a delicate web of life, where each organism plays a crucial role in the intricate dance of survival and sustenance.
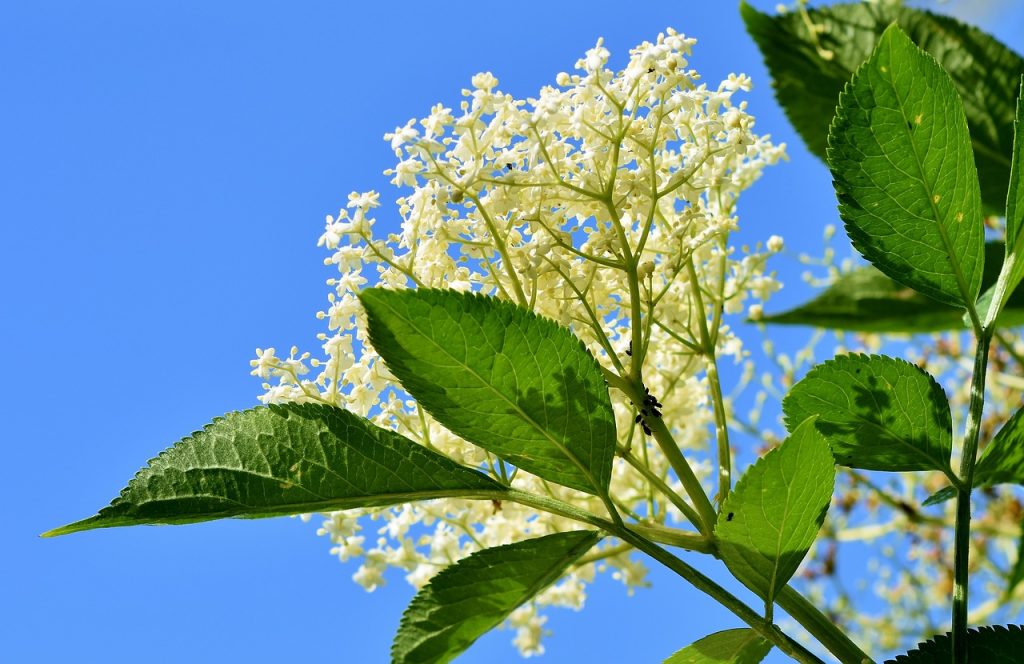
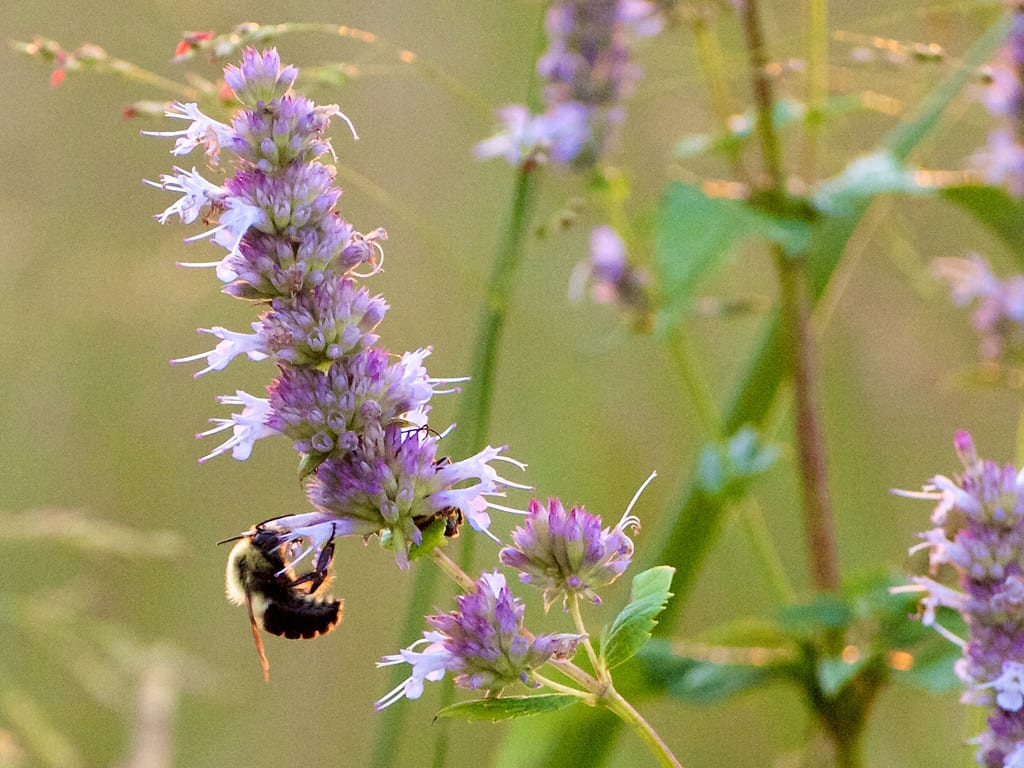
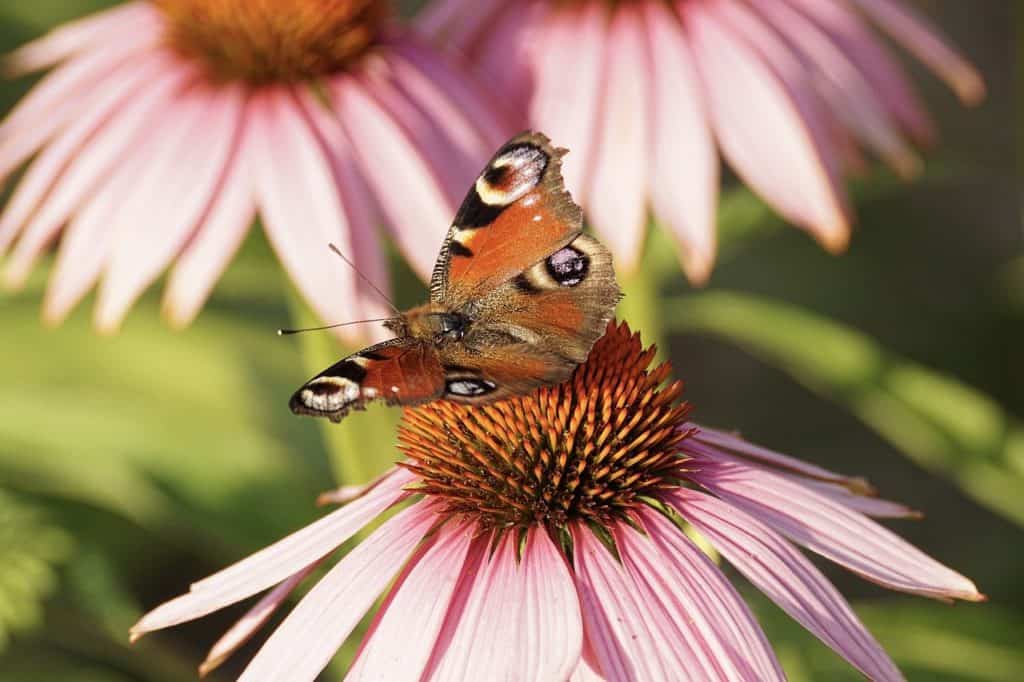
One critical aspect of this balance is the mutual dependence among different species. Pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, diligently transfer pollen from one plant to another, ensuring flora’s reproduction and genetic diversity. In turn, the plants provide nectar and other resources that support the pollinators’ survival. This symbiotic relationship not only secures the continuation of plant species but also contributes to the diverse food web within the ecosystem.
Another crucial component is the regulation of prey populations by predators. Predators, like carnivores and birds of prey, help control the abundance of herbivores and other prey species. This regulation prevents overgrazing and maintains the balance in plant populations, allowing vegetation to flourish without being decimated. In the absence of predators, prey populations may explode, leading to resource depletion and ecosystem instability.
Furthermore, the interconnectedness of all organisms within the habitat ensures that resources are efficiently utilized. The waste produced by one species becomes a valuable resource for another, creating a cycle of sustainability that fosters a harmonious coexistence of life.
We promote a healthier and more robust ecosystem by preserving and maintaining these natural relationships. Such ecological balance bestows numerous benefits, including increased resistance to environmental changes and disturbances. When faced with natural disasters or human-induced alterations, a well-balanced ecosystem can more effectively absorb shocks and recover from disruptions.
Recognizing the importance of ecological balance and resilience, conservation efforts become paramount. Protecting and restoring native habitats not only safeguards endangered species but also preserves the complex web of life that sustains us all. Through understanding and nurturing the delicate relationships in these ecosystems, we can forge a more sustainable future for our planet and the generations to come.
The Importance of Pollinators
Pollinators, which include a diverse array of bees, butterflies, birds, and bats, hold paramount significance in the intricate tapestry of our ecological systems. Their role as facilitators of plant reproduction by transferring pollen between flowers plays a vital part in the circle of life. This essential process directly enables the production of fruits, seeds, and nuts, which, in turn, supports the entire food chain and intricate food webs within ecosystems.
The far-reaching impact of pollinators on the natural world cannot be overstated. Their diligent work enables the cross-fertilization of plants, and localized adaptations, leading to increased genetic diversity and healthier plant populations. This, in turn, translates into a more resilient and vibrant ecosystem that can better withstand environmental challenges and adapt to changing conditions.
Beyond their contributions to the natural world, pollinators play a critical role in sustaining human life as well. About one-third of the world’s food production depends on pollination, with many fruits, vegetables, and nuts relying on these industrious creatures to bear fruit. By supporting the pollinators’ survival and creating native habitats that cater to their needs, we safeguard the sustainability of agricultural practices and the availability of nutritious food for people around the globe.
However, pollinators face numerous threats that endanger their populations. Habitat loss due to urbanization, intensive agriculture, and deforestation reduces the availability of suitable environments for these vital species. Pervasive pesticide use and pollution further compound the challenges they encounter.
To address these pressing issues and safeguard pollinators, conservation efforts are of utmost importance. Planting diverse and pollinator-friendly native gardens, even in urban areas, can provide crucial stepping stones for their movement and sustenance. Reducing pesticide usage and adopting sustainable farming practices also go a long way in supporting our wildlife.
Educational initiatives and community involvement play a significant role in promoting pollinator conservation. Raising awareness about the importance of pollinators and the threats they face can inspire people to take action in their daily lives. Creating pollinator-friendly spaces in backyards, schoolyards, and public areas not only helps these species but also enhances the overall beauty and biodiversity of the landscape.
Pollinators stand as irreplaceable pillars in the intricate balance of nature. Their role in facilitating plant reproduction reverberates throughout the ecosystem, sustaining life in all its forms. By understanding and valuing the importance of pollinators, we can cultivate a harmonious coexistence with these remarkable creatures, ensuring a thriving and sustainable world for generations to come.
Enhancing Ecosystem Services
Preserving and Enhancing Ecosystem Services
The preservation and expansion of native habitats play a vital role in providing essential ecosystem services that directly impact human well-being and the overall health of the environment. These diverse habitats offer an array of invaluable services that contribute to a sustainable and thriving planet.
One prime example is the remarkable ability of wetlands to act as natural water purifiers. Their unique structure and biological diversity enable them to filter pollutants and enhance water quality. By preserving wetlands, we protect the delicate balance of these ecosystems and secure clean and safe water sources for communities and various aquatic species.
Similarly, forests emerge as crucial players in mitigating climate change. Through the process of carbon sequestration, they absorb and store vast amounts of carbon dioxide, thus reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere. By safeguarding existing forests and undertaking reforestation efforts, we bolster their capacity to combat climate change and foster a healthier planet for future generations.
Grasslands, too, offer essential services for environmental stability. Their extensive root systems act as natural barriers against soil erosion, preventing valuable topsoil from being lost to wind or water. Preserving grasslands ensures the retention of fertile soil, essential for agriculture and maintaining the productivity of the land.
Furthermore, native habitats support many other ecosystem services, such as regulating local climates, pollinating crops, and natural pest control. These services are integral to agricultural productivity, ensuring bountiful harvests and food security for human populations.
By actively preserving and enhancing native habitats, we amplify the capacity of these ecosystems to provide critical services that improve human livelihoods and the health of the planet. Conservation efforts to protect biodiversity, restore degraded habitats, and promote sustainable land-use practices are key to achieving this goal.
Recognizing the intrinsic value of native habitats goes hand in hand with understanding their crucial role in supporting life on Earth. By valuing and respecting these ecosystems, we can forge a path towards a more sustainable future, where the harmony between humans and nature thrives, and the legacy we leave behind is one of responsible stewardship for generations to come.


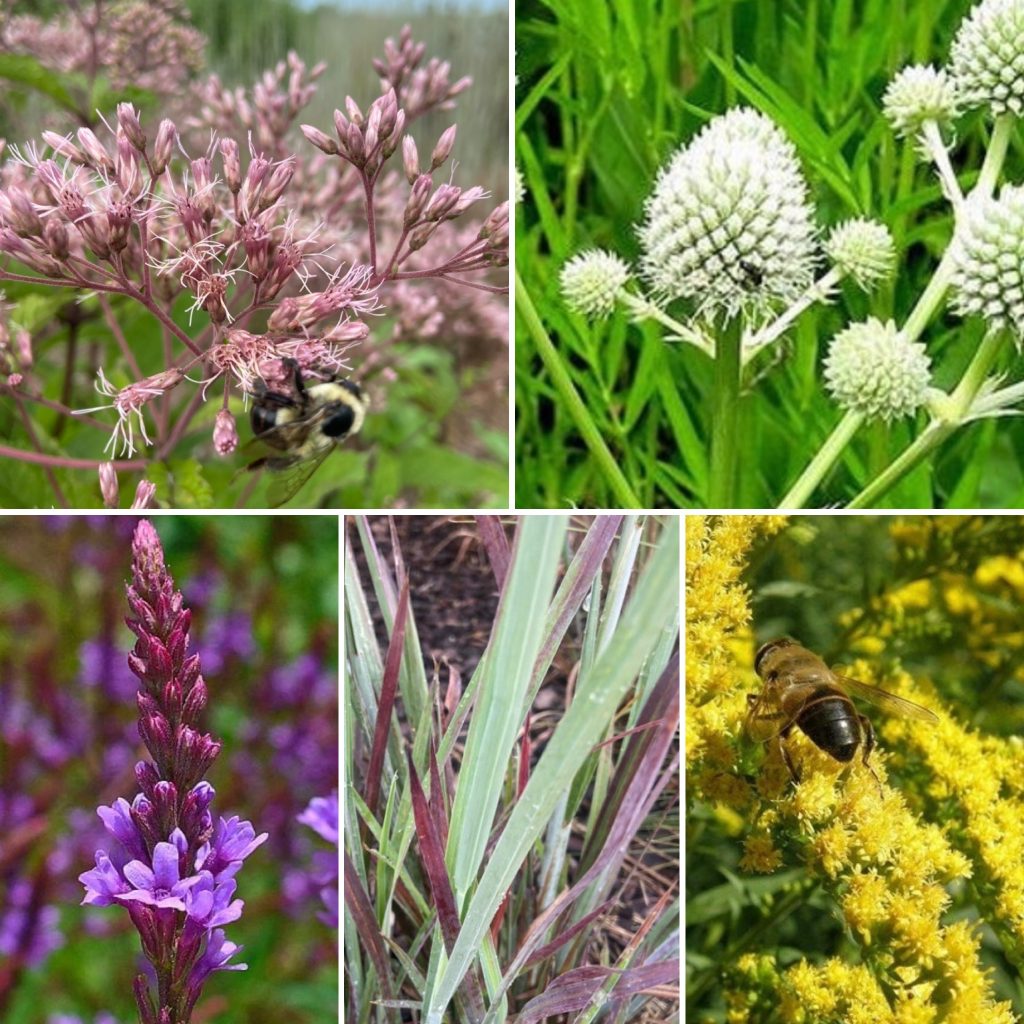
Educational and Recreational Opportunities
Expanding Educational and Recreational Opportunities through Native Habitats
The creation of native habitats not only benefits the environment but also opens up valuable opportunities for education and recreation. Preserved natural areas offer a unique and immersive learning experience, connecting people with the wonders of the natural world and fostering a deep appreciation for biodiversity. By engaging with these habitats, individuals develop a profound understanding of the delicate interplay between various species and their environments, making them more likely to become passionate advocates for conservation efforts.
Educational programs and guided tours within native habitats provide hands-on experiences that allow people to witness the intricate web of life in action. Observing pollinators buzzing among flowers or witnessing wildlife going about their daily routines can be both captivating and enlightening. By offering these immersive experiences, we empower individuals to understand the vital role of each living being and the significance of preserving these habitats for the well-being of all species, including our own.
Furthermore, native habitats serve as excellent outdoor classrooms for students of all ages. They provide a living laboratory for ecological studies, enabling learners to grasp complex concepts firsthand by witnessing nature’s interconnections. Through these experiences, young minds cultivate a sense of responsibility towards the environment and become motivated to make positive changes in their daily lives.
Recreationally, native habitats offer a refuge from the fast-paced urban environment, providing a serene and rejuvenating escape for people seeking solace in nature. Hiking trails, bird-watching spots, and wildlife observation points become gateways to reconnecting with the natural world and reaping the mental and physical health benefits that nature provides.
Creating diverse and thriving habitats is not just an environmental imperative; it is a moral responsibility. By recognizing the intrinsic value of all living beings and understanding the delicate interconnectedness of ecosystems, we can pave the way for a sustainable and harmonious coexistence with nature.
The preservation and restoration of these habitats signify hope for a more resilient and biodiverse future. A future where both humans and the natural world can thrive together in harmony must act now to safeguard the delicate tapestry of life on our planet, ensuring a brighter tomorrow for generations. By collectively embracing our role as stewards of the Earth, we can leave a lasting legacy of responsible conservation and sustainability, preserving the beauty and wonder of nature for future generations to cherish and enjoy.
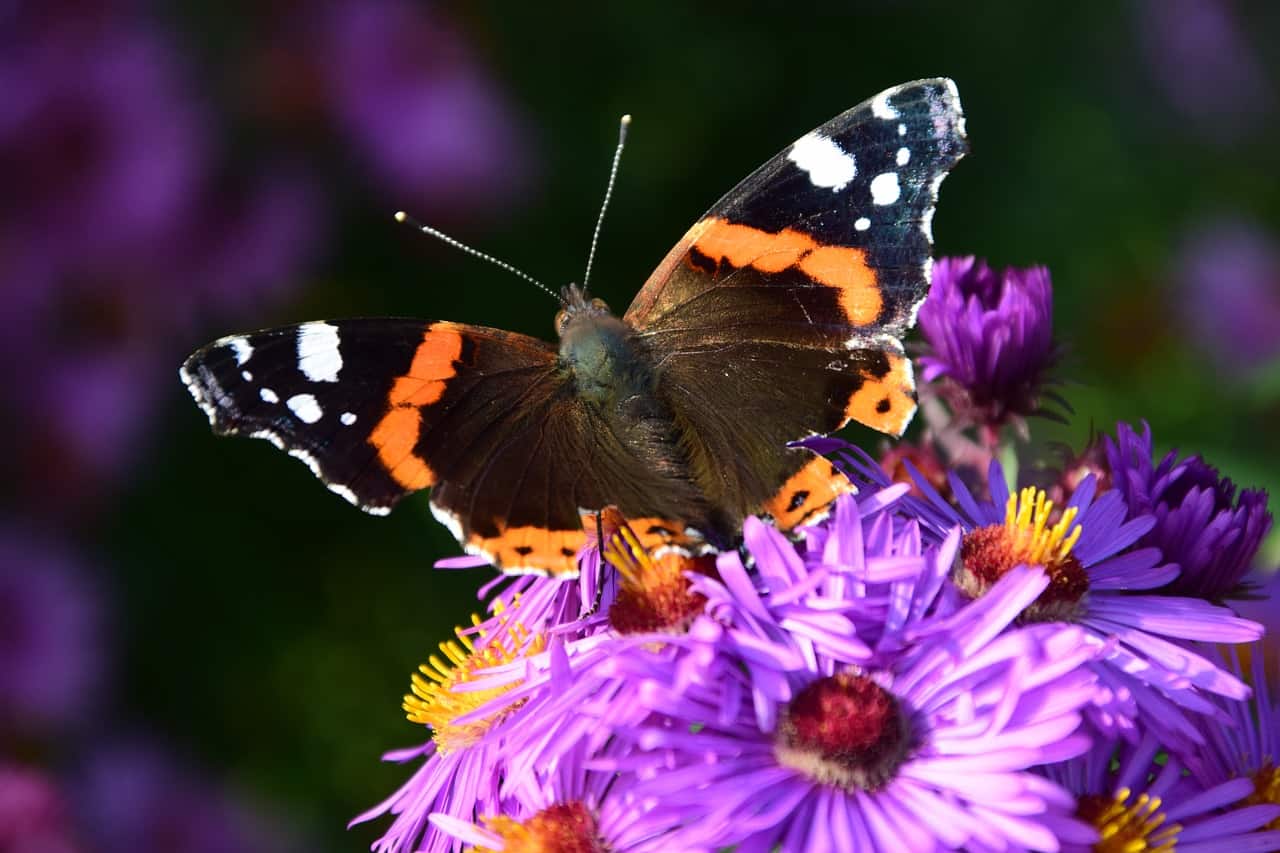
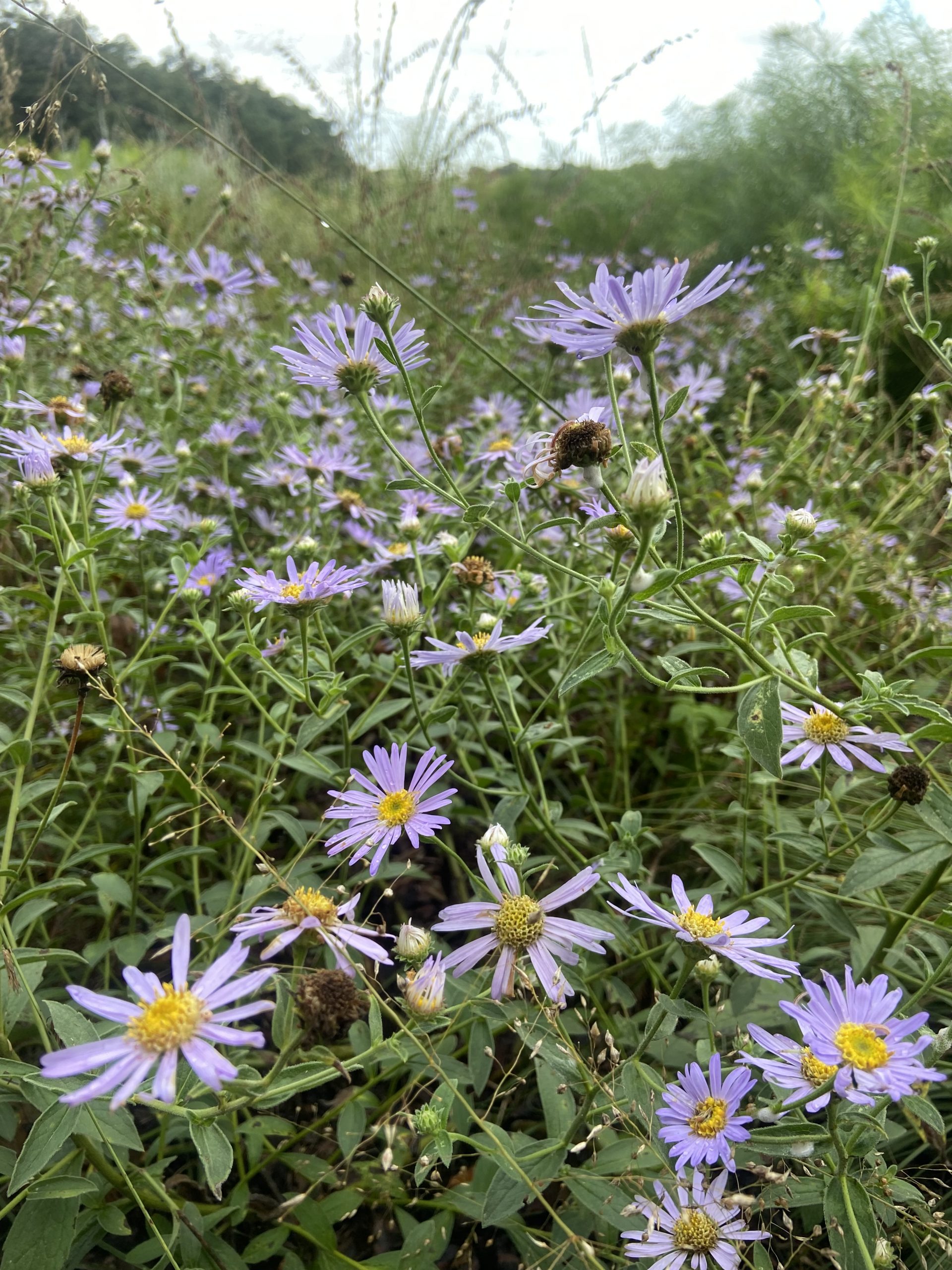



My Grateful Gardening approach!
Gardening with nature is about sustainability and gratitude in a garden setting, making environmentally friendly choices and giving nature a helping hand to support the eco-system around you.
Uses native trees, shrubs and perennials with pops of seasonal color from annuals to achieve a wild flower haven for birds, bees and butterflies as if created by mother nature herself. As garden stewards we are responsible for re-greening the planet and the time is start is now!
Make enviromentally friendly changes and not only improve the quality of you and your families life, but also enable the life of benefical wildlife that one called your garden home.
Epiphany aside, we are blessed to have wildlife visit our gardens, to often I hear complaints over plant losses due to deer, rabbits and ground-hog, I am left considering grateful to have these visit my garden.
Maniciured lawns, heavily mulched beds, chemicals and poisions lingering in the air, has no-place in my garden and I vow to find natural methods to control nusicance insects in my yard, but all are welcome and come they do!
A Raccoon, Box, and Snapper turtles, Hairy & Greater Spotted Woodpeckers, Mockingbirds, A lively Bluejay family, and plentiful songbirds. Bats, Deer, Toads, Frogs, Snakes, and an even groundhog.
Stephen Pryce Lea



